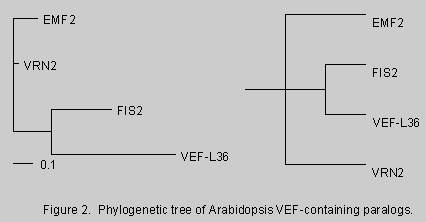
Phylogenetic analysis of Arabidopsis VEF gene family
Arabidopsis proteins VERNALIZATION2 (VRN2), EMBRYONIC FLOWER2 (EMF2), and FERTILIZATION INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM2 (FIS2) share similar VEF domain to Drosophila PcG protein Su(z)12. The three plant proteins show diverse functions via repression of distinct MADS-box genes. The small VEF domain-containing gene family appears to exist extensively in angiosperm. In particular, widespread distribution of EMF2 homologs in angiosperm indicates that their early version occurred after dicots and monocots diverged. Global homology strongly suggests that VRN2 is an abbreviated version derived from an ancestral EMF2. The unique domain organization in FIS2 suggests that it belongs to other lineage in the VEF family. Intragenic sequence repeats and intergenic exon shuffling found between EMF2/VRN2 and FIS2 should account for their functional divergence. EMF2, the family member most similar to genes in other plants and animals, may have played a critical role in the origin of vegetative development. We are investigating the sequences of EMF2 homologs in basal angiosperm, moss, and other early emerging plant species in order to gain insights into the evolution and diversification of the plant species.